
The Finance Minister of India, Ms Nirmala Sitharaman announced on Friday September 20, 2019 a substantial Corporate Tax Rate cut to boost the economic development of India. Since Corporate Tax also called corporation tax or company tax, is a direct tax, the changes in its rates will not impact the GST rates as Goods & Services Tax remains an indirect tax. Important changes in Corporate Tax as announced by the Finance Minister of India include the reduction of corporate tax rate to 22% from 30% while for new manufacturing companies it has been cut down to 15% from 25%.
GST is one of the hot topics and an MBA aspirant should be able to present the facts on the same along with his/her views coherently. Experts at MBAUniverse.com bring forth key facts on this hot GD topic to help an MBA aspirant to take his/her view point while speaking in the GD round of a top MBA college.
Key Updates on GST
- Exporters who have received capital goods under the EPCG scheme are allowed to claim the refund of the IGST paid on exports
- TCS to be collected at the rate of o.5% under CGST Act on the value of net taxable supplies. Similarly, Rate of 0.5% under SGST Act. The total rate of TCS will be 1%
- TDS provisions under GST are effective from October 1, 2018. The council has also specified such persons or category of persons who will be liable to these provisions. Thet are - an authority or board or any other body set up by an Act of parliament or a state legislature orestablished by any government with 51% or more participation by way of equity or control; the society established by the central government or state government or any local authority; Public sector undertakings
- Directorate General of Safeguards will be called Directorate General of Anti-profiteering
Impact of fiscal and monetary policy changes on economy is more relevant to understand whether it would bring with it a wheel of growth or could prove against the economic and business interests of the country, an MBA student is supposed to know and must be able to speak about it in the GD round after gathering thought and analyzing the pros and cons of the same.
What is the GST
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is an indirect tax applicable throughout India which has replaced multiple cascading taxes levied by the Central and State governments. GST was introduced as The Constitution (One hundred and first Amendment) Act 2017 following the Constitution 122nd Amendment Bill. The GST is governed by a GST Council and its Chairman is the Finance Minister of India. The process of forming the legislation took 17 years. It was first proposed in the year 2000. The minimum tax rate under GST is 0% and highest tax rate is 28%.
Key Facts
- Under GST, Goods and services are taxed at the following rates: 0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, 28%.
- There is a special rate of 0.25% on rough precious and semi-precious stones and 3% on gold. In addition a cess of 15% or other rates on top of 28% GST applies on few items like aerated drinks, luxury cars and tobacco products.
- A single GST has replaced several existing taxes and levies which include: central excise duty, services tax, additional customs duty, surcharges, state-level value added tax and Octroi.
- Other levies which were applicable on inter-state transportation of goods have also been done away with the launch of GST regime.
|
Group Discussion Topics & Tips: Learn the Facts
|
Activities covered under GST
GST is levied on all transactions such as sale, transfer, purchase, barter, lease, or import of goods and/or services. India has adopted a dual GST model implying that taxation is administered by both the Union and State Governments.
Transactions made within a single state will be levied with Central GST (CGST) by the Central Government and State GST (SGST) by the government of that state. For inter-state transactions and imported goods or services, an Integrated GST (IGST) is levied by the Central Government.
GST is a consumption-based tax the impact of which will be at the destination. The taxes therefore, are paid to the state where the goods or services are consumed and not the state in which they were produced.
IGST complicates tax collection for State Governments by disabling them to collect the tax owed to them directly from the Central Government. Under the previous system, a state would have to only deal with a single government in order to collect tax revenue.
GST: Why Differential tax rates are applied?
- Lower rates for essential items and the highest for luxury and de-merits goods.
- Service Tax has gone up from 15% to 18%. The services are taxed at lower rates such as train tickets and will fall in the lower slabs.
- Essential items including food is taxed at zero rate. The propose is to control inflation as food and essential items constitute roughly half of the consumer inflation basket.
- The lowest rate of 5% is for common use items. There are two standard rates of 12 per cent and 18 per cent, which fall on the bulk of the goods and services. This includes fast-moving consumer goods.
- Highest tax slab is applicable to items which are currently taxed at 30-31% - excise duty plus VAT.
- Ultra luxuries, demerit and sin goods like tobacco and aerated drinks attract a cess for a period of five years on top of the 28 per cent GST. The collection from this cess as well as that of the clean energy cess would create a revenue pool which would be used for compensating states for any loss of revenue during the first 5 years of implementation of GST. The cess would be lapsable after 5 years.
- The structure is a compromise to accommodate demand for highest tax rate of 40% by states like Kerala.
- The principle for determining the rate on each item is to levy and collect the GST at the rate slab closest to the current tax incidence on it.
The Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN)
Government has created GSTN as a non-profit organization. As per the government website on GST, "Goods and Services Tax" Network (GSTN) is a nonprofit organisation proposed to be formed for creating a website / platform for all the concerned parties related to the GST, namely stakeholders, government and taxpayers to collaborate on a single portal. When up and running, the portal is supposed to be accessible to the central government which allows it to track down every transaction on its end while taxpayers are advertised to have the ability of connecting this to their tax returns. However its efficacy and efficiency is yet to be tested. The IT network was touted to be developed by unnamed private firms. The known authorised capital of GSTN is ₹10 crore (US$1.6 million) in which Central Government holds 24.5 percent of shares while the state government holds 24.5 percent and rest with private banking firms for smooth running of the transactions.
GST Launched WEF July 1, 2017
After a long nationwide debate on Goods and Service Tax (GST), the initiative was launched at midnight on June 30, 2017 in a ceremony held at Central hall of Parliament. Various provisions and benefits of GST were shared in their speeches by the Finance minister of India, Mr Arun Jaitley; the Prime Minister of India Mr Narendra Modi and the President of India Shri Pranab Mukherjee.
India’s biggest tax reform was launched at midnight of June 30 at Parliament's historic Central Hall, by President Pranab Mukherjee and Prime Minister Narendra Modi. GST therefore, became effective from July 1, 2017.
Current tax rates were replaced by GST rates with effect from July 1. It is the fourth time since Independence that an event was held at the Central Hall of Parliament at midnight. The last three celebrated India's Independence. Congress boycotted the GST launch along with several other opposition parties. GST replaced a slew of indirect taxes with a unified tax and was set to dramatically reshape the country's 2 trillion dollar economy.
The Cheaper and costlier after GST launch
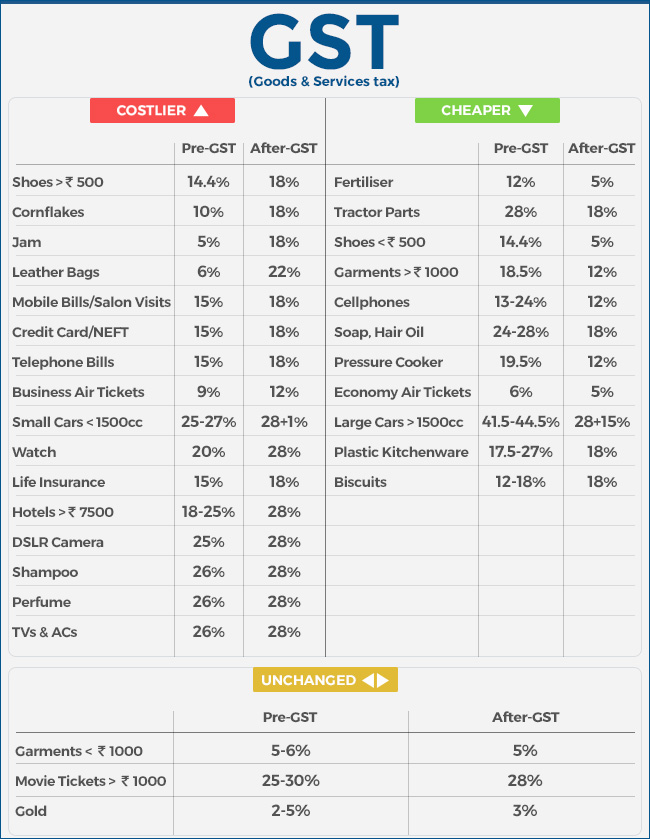
Source: NDTV
Inflationary impact
The GST fuelled inflation in the short term. The GST rate started at 5% and went upto 28%. The 18% taxation on services such as restaurants; movies increased prices. Another problem with the GST is not including liquor and petroleum under GST’s ambit. These are major revenue sources for the government.
After the introduction of the GST, while costs of essential food items did not increase so much, other consumer goods and services in India including food, hotel charges, insurance and cinema tickets have become costlier. Upon its introduction in the country, GST led to a number of protests by the business community, primarily due to an increase in overall taxes and hence the prices of goods. Thousands of cinema theatres in the states where higher rate of GST was applied on movie tickets went on strike.
However, with the launch of GST, the check posts across the country were abolished ensuring free and fast movement of goods. The central government has assured states of compensation for any revenue loss incurred by them from the date of GST for a period of five years. However, no concrete laws have been framed to support such action.
Taxes replaced by GST
The following taxes have been replaced by the GST:
- Central Excise Duty
- Commercial Tax
- Value Added Tax (VAT)
- Food Tax
- Central Sales Tax (CST)
- Introit
- Octroi
- Entertainment Tax
- Entry Tax
- Purchase Tax
- Luxury Tax
- Advertisement tax
- Service Tax
- Customs Duty
- Surcharges
GST Calculation
Assume that the GST is set at 20%. Suppose that the manufacturing cost of a Product A is 100 and assuming a GST of 20% the total amount is Rs. 120. The next step of taxation would be when the Product is sold to consumers. Suppose the product is sold at a price of 150. The GST will charge another 20% on just the difference of Rs. 150 and Rs. 120 i.e. only 20% on Rs. 30 which is equal to Rs. 6. Accordingly, the final price is Rs. 150 + Rs. 6. GST will be applied at every step of value creation. The GST is estimated to provide an immediate boost of 0.9% – 1.4% of the GDP.
GST is in a form of comprehensive indirect tax on manufacturing, sales and consumption of goods and services within the country. It is based on the input tax method. The tax is levied and collected at each stage of sale or purchase of goods or services.
Benefits of GST
- GST is a right step to move forward with the ‘Make in India’ vision. GST gets rid of multi tier and multiple taxation system in the country
- GST-registered businesses will be able to claim tax credit to the value of GST they paid on purchase of goods or services as part of their normal commercial activity.
- GST is a destination based tax as against the present concept of origin based tax. The tax structure is much simpler and easier to understand.
- According to a report by the National Council of Applied Economic Research, GST is expected to increase economic growth by between 0.9 per cent and 1.7 per cent.
- Taxable goods and services are not distinguished from one another and are taxed at a single rate in a supply chain till the goods or services reach the consumer.
- Reducing production costs will make exporters more competitive. The reduced cost of locally manufactured goods and services will increase the competitiveness of Indian goods and services in the international market
- GST eliminates complexities in the present taxation structure and consequently prevent the loss of nearly 50% of the advantage of lower manufacturing costs that India has over the western nations
- Single authority will have the administrative responsibility to levy tax on goods and services
- Implementation of GST assures a single taxation system in the entire country for all goods and services making tax compliance easier and more effective
Adverse effects
- GST is said to be proving detrimental to the growth of small scale industries. Basic exemption limit in excise of Rs. 1.5 Crores taken away in GST, which affects the Small Scale Industries. Lakhs of industries in India are surviving only for one reason that they are not required to pay excise if their turnover does not exceed 1.5 crores.
- Services which were charged on receipt basis are charged on accrual basis.
- GST is required to be paid, once invoice is raised even if there is no certainty of receiving the payments for the services rendered
- Number of goods and services have become costlier after launch of GST. It would increase inflation in the country which is already reeling under the pressure of demonetization.
Changes in GST
Barely three months after rolling out the Goods and Services Tax, Finance Minister Arun Jaitley, who heads the council, also announced businesses with a turnover of up to 1.5 crores would be allowed quarterly filing of GST Return.
Key points of change in GST regime
Small and Medium traders and exporters were hurt most by the application of GST. It was crucial to Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s plans to create millions of more jobs. Accordingly, the decisions were taken with a view to raise revenue and ease compliance. Following are the major changes in GST implementation taken to boost the growth rate of Indian economy and provide an environment for ‘Ease of doing Business’.
- Businesses with less than 1.5 crores annual turnover will file returns and pay taxes on a quarterly basis instead of monthly basis. Such businesses make up for nearly 90 per cent of tax assesses but contribute very little tax.
- The GST council also agreed to raise the threshold for the composition scheme. This scheme allows small traders to pay a standard tax rate – from Rs. 75 lakh in turnover to Rs. 1 crore. These establishments pay standard tax rates; 1 per cent for traders, 2 per cent for manufacturers and 5 per cent for restaurants.
- Reverse charge mechanism suspended till March 2018. This rule shifts the liability to pay the tax on the buyer rather than the seller and the supplier has to be registered under GST to check tax evasion.
- The GST council agreed and advised the government to start issuing refund cheques from 10 October to exporters who had complained their working capital was locked up. By April 1, 2018, the council also targeted to have e-wallets for every exporter to credit a notional amount as an advance credit to pay taxes.
- The GST rates for textiles including zari, unbranded ayurvedic medicines, plastic and e-waste have been slashed by the council. The council comprises state finance ministers, officials from both states and the Centre and is headed by Union Finance Minister.
- The RBI governor has suggested simplifying GST to boost growth and earlier cautioned also that “teething problems” with GST had impacted the manufacturing sector.
- GST Council decided to defer registration of tax deduction and collection at source till March 31, 2018. Goods transporters who had threatened to go on strike, have been told services provided to unregistered entities would be exempted from GST.
The Prime Minister, Mr Modi has also promised to fix problems in GST cited by businesses.
Reduced GST rates
GST rates for certain Goods and IGST rates on Imports of specified Goods were reduced shortly after the launch of GST:
A. GST RATE FOR FOLLOWING GOODS HAVE BEEN REDUCED
|
S.
No.
|
Chapter/
Heading/
Sub-heading/
Tariff item
|
Description
|
Present GST Rate
|
GST Rate Recommended by the GST Council
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1.
|
0804
|
Mangoes sliced dried
|
12%
|
5%
|
|
2.
|
1905 or 2106
|
Khakra and plain chapati / roti
|
12%
|
5%
|
|
3.
|
19 or 21
|
Food preparations put up in unit containers and intended for free distribution to economically weaker sections of the society under a programme dulyapproved by the Central Government or any State Government, subject to specified conditions
|
18%
|
5 %
|
|
4.
|
21
|
Namkeens other than those put up in unit container and, -
(a) bearing a registered brand name; or
(b) bearing a brand name on which an actionable claim or enforceable right in a court of law is available [other than those where any actionable claim or enforceable right in respect of such brand name has been foregone voluntarily
|
12%
|
5%
|
|
5.
|
2710
|
Imposing GST only on the net quantity of superior kerosene oil [SKO] retained for the manufacture of Linear Alkyl Benzene [LAB]
|
18%
|
18%
[Clarification to be issued]
|
|
6.
|
30
|
Ayurvedic, Unani, Siddha, Homeopathy medicines, other than those bearing a brand name
|
12%
|
5%
|
|
7.
|
3213
|
Poster Colour
|
28%
|
18%
|
|
8.
|
3407
|
Modelling paste for children amusement
|
28%
|
18%
|
|
9.
|
3915
|
Plastic waste, parings or scrap
|
18%
|
5%
|
|
10.
|
4004 00 00
|
Rubber waste, parings or scrap
|
18%
|
5%
|
|
11.
|
4017 00 20
|
Hard Rubber waste or scrap
|
28%
|
5%
|
|
12.
|
4707
|
Paper waste or scrap
|
12%
|
5%
|
|
13.
|
4907
|
Duty credit scrips
|
5%
|
Nil
|
|
14.
|
5401
|
Sewing thread of manmade filaments, whether or not put up for retail sale
|
18%
|
12%
|
|
15.
|
5402, 5404, 5406
|
All synthetic filament yarn, such as nylon, polyester, acrylic, etc.
|
18%
|
12%
|
|
16.
|
5403, 5405, 5406
|
All artificial filament yarn, such as viscose rayon, Cuprammonium,
|
18%
|
12%
|
|
17.
|
5508
|
Sewing thread of manmade staple fibres
|
18%
|
12%
|
|
18.
|
5509, 5510, 5511
|
Yarn of manmade staple fibres
|
18%
|
12%
|
|
19.
|
5605
|
Real Zari
|
12%
|
5%
|
|
20.
|
6802
|
All goods falling under heading 6802 [other than those of marble and granite or those which attract 12% GST]
|
28%
|
18%
|
|
21.
|
7001
|
Cullet or other waste or scrap of Glass
|
18%
|
5%
|
|
22.
|
8305
|
Fittings for loose-leaf binders or files, letter clips, letter corners, paper clips, indexing tags and similar office articles, of base metal; staples in strips (for example, for offices, upholstery, packaging), of base metal
|
28%
|
18%
|
|
23.
|
8483
|
Plain Shaft Bearing 8483
|
28%
|
18%
|
|
24.
|
84
|
Parts suitable for use solely or principally with fixed Speed Diesel Engines of power not exceeding 15HP
|
28%
|
18%
|
|
25.
|
84 or 85
|
Parts suitable for use solely or principally with power driven pumps primarily designed for handling water, namely, centrifugal pumps (horizontal and vertical), deep tube-well turbine pumps, submersible pumps, axial flow and mixed flow vertical pumps
|
28%
|
18%
|
|
26.
|
84 or 85
|
E-Waste
|
28%/18%
|
5%
|
|
27.
|
Any Chapter
|
Biomass briquettes
|
18%
|
5%
|
B. IGST EXEMPTION ON IMPORTS OF GOODS:
|
S. No
|
Description
|
Present applicable IGST rate
|
Recommended IGST rate
|
|
1
|
IGST exemption on imports of rigs imported for oil / gas exploration and production projects under lease, subject to the following conditions that:
(i) Integrated tax leviable under section 5(1) of the IGST Act, 2017 on supply of service covered by item 1(b) or 5(f) of Schedule II of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017;
(ii) The rig is not sold without the prior permission of the Commissioner of Customs of the port of importation;
(iii) to re-export the goods within 3 months from the expiry of the period for which they were supplied under a transaction covered by item 1(b) or 5(f) of Schedule II of the Central Goods and Services Tax Act, 2017 out of India;
(iv) to pay on demand an amount equal to the integrated tax payable on the said goods but for the exemption under this notification in the event of violation of any of the above conditions and applicable interest.
|
5%
|
Nil
|
|
2
|
Exemption from IGST on imports of medicines supplied free by international agencies like UNICEF, WHO, Red Cross etc.
|
12%/5%
|
Nil
|
|
3
|
A. Exemption from IGST on imports of bona fide gifts upto CIF value limit of Rs. 5000 imported through post or air.
|
28%
|
Nil
|
GST is levied on all transactions such as sale, transfer, purchase, barter, lease, or import of goods and/or services. India has adopted a dual GST model implying that taxation is administered by both the Union and State Governments.
After the changes in GST rates, it is expected that prices of essential items will stop increasing. The small and medium businesses which saw no growth, would be on the track again and will contribute to the economic growth of the country. Read More Group Discussion Topics
Before Budget 2018: GST rates reduced again
GST Rates for 29 Goods and 53 Services have been reduced. These rates will come into effect from 25th January 2018.
GST Rate Changes for Goods:
Nil Rated Goods:
- Vibhuti
- Parts and accessories for the manufacture of hearing aids.
- De-oiled rice bran
Rates reduced from 28% to 18%
- Old and used motor vehicles [medium and large cars and SUVs] with a condition that No ITC is availed
- Public transport Buses that run on Biofuel
Rates reduced from 28% to 12%
For Old and used motor vehicles [other than medium and large cars and SUVs] with a condition that No ITC is availed
Rates reduced from 18% to 12%
- Sugar boiled Confectionery
- Drinking water packed in 20 litres bottles
- Biodiesel
- Drip irrigation system including laterals, sprinklers
- Mechanical Sprayer
- Certain listed Bio-pesticides (12 in nos)
- Fertilizer grade Phosphoric acid
- Bamboo wood building joinery
Rate reduced from 18% to 5%
- LPG supplied to Household Domestic Consumers
- Raw materials and Consumables needed for Launch vehicles, Satellites and Payloads (Both CGST and IGST Rates)
- Tamarind Kernel Powder
- Mehendi paste in cones
Rates reduced from 12% to 5%
- Articles of straw, of esparto or of other plaiting materials
- Velvet fabric [with a condition that no refund is claimed on ITC]
Rates reduced from 3% to 0.25%
Diamonds and precious stones
GST Rate increased from 12% to 18%
Cigarette filter rods
Rate increased from 0% to 5%
Rice bran (other than de-oiled rice bran)
Compensation cess is reduced to 0% for following motor vehicles :
- Old and used motor vehicles [medium and large cars and SUVs]with a condition that No ITC is availed
- Old and used motor vehicles [other than medium and large cars and SUVs] with a condition that No ITC is availed
- Vehicle that is cleared as an ambulance (having all accessories necessary in ambulance)
- 10-13 seater Buses and ambulances subject to specified conditions
GST Rate Changes for Services:
GST newly applicable on following:
- GST Rate at 5% on small housekeeping service providers, notified under section 9 (5) of GST Act, who provide housekeeping service through ECO, without availing ITC
- GST Rate at 28% on actionable claim in the form of chance to win in betting and gambling including horse racing
Rate reduced from 28% to 18%
Services by way of admission to theme parks, water parks, joy rides, merry-go-rounds, go-karting and ballet
Rate reduced from 18% to 12%
1. Transportation of petroleum crude and petroleum products with ITC Credit.
2. Metro and monorail projects (construction, erection, commissioning or installation of original works)
3. Works Contract Services by Sub-contractor to the Main contractor under the following scenario:
Where the main contractor provides WCS to Central Government, State Government, Union territory, a local authority, a Governmental Authority or a Government Entity at the rate of 12%
Note: Similarly, GST Rate for Sub-contract services to the main contractor shall attract 5% where the Main contractor is providing services to Central Government, State Government, Union territory, a local authority, a Governmental Authority or a Government Entity at the rate of 5%
4. Common Effluent Treatment Plants services for treatment of effluents
5. Mining or exploration services of petroleum crude and natural gas and for drilling services in respect of the said goods
Rate reduced from 18% to 5%
- Tailoring Services
- Transportation of petroleum crude and petroleum products without ITC Credit.
- Job-work services for manufacture of leather goods(Chapter 42) and footwear (Chapter 64)
Following Services are exempted :
- Providing information under RTI Act, 2005 from GST.
- Legal services provided to Government, Local Authority, Governmental Authority and Government Entity.
- Transportation of goods from India to a place outside India by air or sea until 30th September 2018:
- Life Insurance to personnel of Coast Guard (under the Group Insurance Scheme of the Central Government) by the Naval Insurance Group Fund, retrospectively w.e.f. 1.7.2017
- Dollar-denominated services provided by financial intermediaries located in IFSC SEZ, which have been deemed to be outside India under the various regulations by RBI, IRDAI, SEBI or any financial regulatory authority, to a person outside India
- Pure services provided to Government entity by a Panchayat/ Municipality. Composite supply involving predominantly supply of services (i.e. up to 25% of the supply of goods) is also exempted.
- Lease of land:
- By government or local authority to governmental authority or government entity
- Supply as a part of specified composite supply of construction of flats, etc
- Admission to, or conduct of examination provided to all educational institutions including any service of conducting entrance examinations on collection of entrance fees
- Reinsurance services in respect of following insurance schemes :
- General insurance business provided under schemes such as Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojna and others listed in Notification 12/2017-CGST Rate
- Life insurance business provided under schemes such as Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana and others listed in Notification 12/2017-CGST Rate
- Services by way of fumigation in a warehouse of agricultural produce
- Services of admission to planetarium where consideration charged is below Rs.500
- Subscription of online educational journals/periodicals by educational institutions who provide degree recognized by any law
- Renting of transport vehicles to a person providing services of transportation to an educational institution (students, faculty, and staff) providing education upto higher secondary or equivalent.
- Services provided by and to Fédération Internationale de Football Association (FIFA) and its subsidiaries directly or indirectly related to any of the events under FIFA U-20 World Cup in case the said event is hosted by India.
GST is levied on all transactions such as sale, transfer, purchase, barter, lease, or import of goods and/or services. India has adopted a dual GST model implying that taxation is administered by both the Union and State Governments.
After the changes in GST rates, it is expected that prices of essential items will stop increasing. The small and medium businesses which saw no growth, would be on the track again and will contribute to the economic growth of the country.
































