Theme 2018: MBA Pedagogy for 21st Century Business School
Dominant pedagogy at leading B-schools |
||||
|
||||
| Lecture This is the most well known and widely used approach in Indian MBA programs. If the learning outcome of a session is to fill an important gap in student’s knowledge that might be used for later analysis, a lecture format imparts key, and crucial information to be remembered and later recalled. In general, lecturing has a very specific purpose and its most optimal use in the business school context is for presenting complex material, having control over that material, and allowing room for clarification of questions. Technology enabled tools are adding dynamism to the traditional method. Flipped Classroom is one model, where lectures are available online for students to view and class time is focussed on discussions. |
||||
| ISB has developed a tool for understanding the effectiveness of class room teaching. Students get a short quiz
on their laptops mid-way into a session, and they are supposed to answer the questions instantly. Faculty gets
instant feedback on the comprehension of the concept being taught. Case Method Pioneered by Harvard Business School, the Case Method is a thoughtful educational innovation that presents the challenges confronting leading companies or any other organizations, alongwith with the constraints and usually incomplete information found in real world scenario and places the student in the role of the protagonist/decision maker. There are no simple solutions; yet through the dynamic process of exchanging perspectives, countering and defending points, and building on each other's ideas, students become adept at analyzing issues, exercising judgment, and making difficult decisions. In India, while IIM Ahmedabad pioneered the method, data seems to suggest that many other B-schools like IIM Indore and NMIMS are placing higher focus on it today. Simulation Business simulations like CAPSIM, CESIM, Markstat, Brandpro, Beer game and many others are software that model the processes that occur in a specific industry or environment. While certain parameters are fixed to create a baseline environment for participants, others can be changed by students or groups of students depending on the outcomes they want, and the learning that students should be able to take away. One of the most popular simulations, Markstrat, developed by Prof Jean-Claude Larréché at INSEAD, is used as a simulated scenario for learning concepts such as Brand Portfolio Strategy, as well as how to manage marketing profits, and work in a highly competitive environment. Use of Simulation is limited in Indian B-schools due to lack of trained faculty and expensive software licences. Research on their efficacy in Indian context is also not readily available. |
||||
|
||||
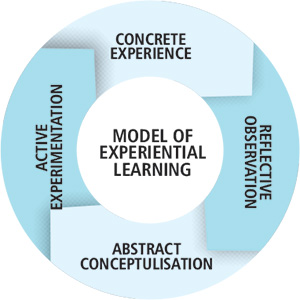
| HBS’ Field Immersion Experiences for Leadership Development (FIELD) is another example of experiential
learning initiative at top B-schools. Lead by XLRI and SPJIMR a lot of B-schools in India are putting greater emphasis on Experiential Learning. SPJIMR says its Non-Classroom Learning (NCL) offers three distinct levels of learning: Self-Awareness, Self- Management and Societal Awareness. It has five NCL initiatives towards these goals: Abhyudaya, ADMAP, DOCC, PG Lab and Science of Spirituality. Himalayan Outbound Programme (HOP) at IIM Indore is another example of recent experiential learning initiatives in Indian context. Started in 2010 as an experiment with just 30 students, the course was formally inducted into the second-year curriculum as a 4-credit course. Every year since then, the programme takes place across various popular Himalayan trek routes. The students go through multiple rounds of training, focusing on adventure sports and real-life challenges, designed to test their managerial and leadership skills. Learning Goals for MBA Graduates At this stage, let’s remind ourselves that Pedagogical Innovations in isolation are merely a dangerous fad. Pedagogy (as well as Curriculum Content) cannot be thought about in isolation of the goals it aims to achieve. So, while thinking about Pedagogy of a Business Program, defining Learning Goals is key. What are Learning Goals? AACSB defines them as “Learning goals state the educational expectations for each degree program. They specify the intellectual and behavioural competencies a program is intended to instil. In defining these goals, the faculty members clarify how they intend for graduates to be competent and effective because of completing the program.” Learning Goals are achieved by getting the “content”, “pedagogy”, and “structure” or “architecture” right. Learning Goals: A few examples In Rethinking the MBA, after interviewing hundreds of Executive and Deans, authors layout following “unmet needs” which also be potential learning goals: • Gaining a global perspective • Developing leadership skills • Gaining a global perspective • Developing leadership skills • Honing integration skills • Recognizing organizational realities and implementing effectively • Acting creatively and innovatively • Thinking critically and communicating clearly • Understanding the role, responsibilities, and purpose of business • Understanding the limits of models and markets ISB puts following as Program Learning Goals of its PGP program: • Interpersonal Awareness and Working in Teams • Critical and Integrative Thinking • Awareness of Global Issues Affecting Business • Effective Oral Communication• Ethical Responsibility IIM Indore has set following eight Learning Goals for its PGP Program: • Enable students to understand relevance of context in business • Develop social consciousness • Develop critical thinking skills• Inculcate integrative thinking ability • Promote interpersonal awareness and ability to work in groups • Enable students to learn how to apply the basic principles of communication in order to write effective business messages, case analysis and reports. • Develop competence in quantitative analysis • Prepare business leaders with a sound understanding of ethics Undoubtedly there could be many other objectives and goals. After determining your MBA Program goals, the next step is to determine the right curriculum and pedagogy for achieving your goals. IMC 2018 shall focus on exploring pedagogy mix and approaches for developing two specific learning goals: 1. Domain/ Job-Role experts with high employability skills 2. Innovative & Creative Problem Solvers IMC 2018 Speakers and IMC Awards Case-studies will offer insights on Pedagogy for meeting above goals. |
||||
|